The retail industry continues to be impacted by digital transformation, steep competition, market saturation, supply chain disruptions, and economic complexity. If that’s not enough, the industry must manage constantly shifting customer expectations and demands. As retail players in the e-commerce and physical spaces continue to adjust their strategies, they’re turning to Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology to enhance customer experiences, streamline operations, and boost sales. How is AI transforming the retail sector? Let’s dive in.
Key Challenges the Retail Sector is Facing
Digital transformation and steeper competition
E-commerce players, particularly giants like Amazon, continue driving changes and transformation in retail. The shift to online shopping accelerated greatly during the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2023, online sales accounted for 19% of total retail sales worldwide and are expected to account for 23% of total retail sales worldwide by 2027.
What does it take to survive and thrive in retail today? It comes down to a strong online presence and omnichannel strategy. And it’s large e-commerce companies that set the standard for customer service and speed. As consumers become accustomed to a personalized, convenient shopping experience from these large e-commerce companies, they expect the same experience from all retailers across the board.
So, it’s no surprise that advanced technologies, including AI and machine learning, are increasingly used for demand forecasting, supply chain management, and inventory management to better meet consumer expectations. Likewise, retailers increasingly leverage data science with customer data to meet shifting consumer expectations and provide personalized product recommendations.
Supply chain disruptions
Global supply chain complexity continues to impact the retail industry. Disruptions, such as those caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, can significantly affect inventory and lead times. Of course, customers are quickly turned off by brands that lack inventory and have slow delivery times. Many retailers continue to look for ways to make their supply chains more efficient and resilient, with top tactics including diversifying suppliers and increasing onshore production.
Economic volatility
At the same time, the retail sector is sensitive to economic fluctuations. Economic downtowns and changes in consumer spending can quickly affect retail sales. Rental prices for physical retail spaces can also fluctuate, impacting overheads and profit margins. It’s not uncommon for retailers to reimagine physical stores as showrooms or experience centers (rather than traditional sales spaces). Balancing brick-and-mortar and e-commerce operations is crucial for retailers to optimize costs and customer reach. On top of it all, retailers must be agile and adjust to these shifts quickly. That means having access to the right data and forecasting capabilities.
How AI Is Helping Transform the Retail Industry

As these challenges grow, retail technology executives have begun to apply AI to innovate and improve their organizations’ operations. One of the areas where AI and data science have already made a notable impact is customer experience. Consider these customer-facing benefits:
- Personalization: AI can analyze customer data to predict preferences and suggest products for highly personalized shopping experiences.
- Customer service: To meet customer expectations for speed and convenience, retailers can use AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to provide 24/7 customer service.
- Shopping experience enhancement: Retailers can also use AI to optimize store layouts and product placements by generating heat maps of in-store traffic, which enhances the shopping experience.
AI is also being used to optimize the supply chain and alleviate pressures through:
- Demand forecasting: AI can more accurately predict future product demand by analyzing hundreds of demand drivers and data sources, including market trends, historical sales data, weather trends, and social media sentiment.
- Inventory management: Retailers use AI to optimize stock levels, reducing overstocks and stockouts. This helps improve cash flow, reduce storage costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Marketing and sales are another popular area for AI utilization, particularly through:
- Targeted marketing: AI analyzes customer behavior to enable targeted marketing campaigns, which can increase conversion rates and customer retention.
- Price optimization: AI algorithms can dynamically adjust prices based on demand, inventory levels, and competitor pricing.
- Product discovery: AI also enables visual search capabilities on e-commerce sites and apps, allowing customers to upload their own product images to find similar products from a website, improving product discoverability.
- Trend forecasting: Retailers can use AI to analyze trends and predict what products will be popular to stay ahead of the curve in product and stock decisions
In addition, AI can enhance fraud detection and prevention. AI can detect unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent transactions, such as multiple orders with different names coming from the same address or high volumes of costly returns. By identifying and flagging these transactions, retailers can reduce losses due to fraud.
AI Case Studies in the Retail Sector
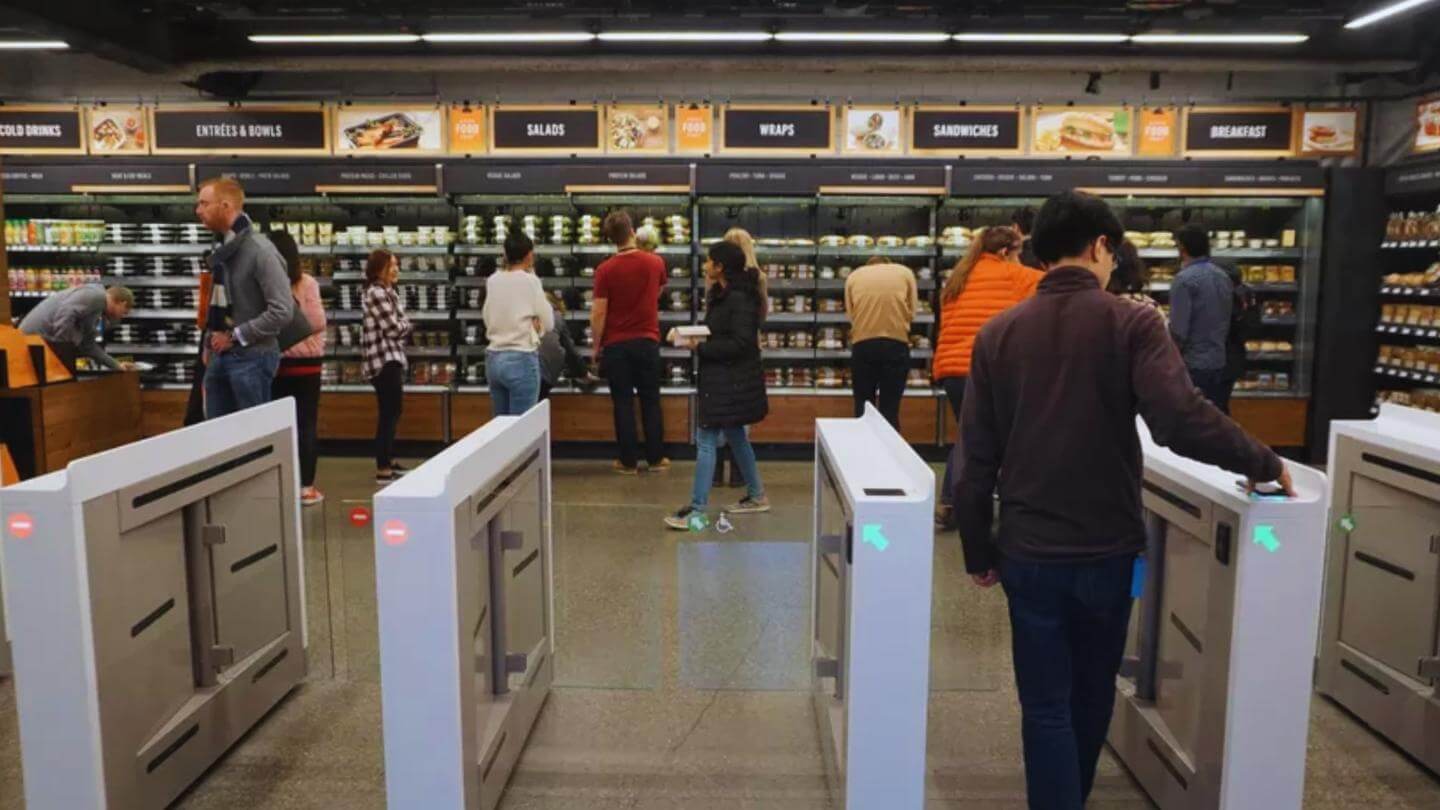
Amazon Go is one of the retail industry’s most significant AI use cases around customer experience. The public automated brick-and-mortar store supports cashless checkouts to reduce the frustration around queuing to check out. The stores utilize a computer vision-enabled camera system supported by lightning-fast data processing (thanks to edge computing) to empower shoppers to walk in, pick up items, and leave without going to the checkout. What originally launched as a “Just-Walk-Out” store in Seattle has expanded across supermarkets and sports arenas, including at Globe Life Field (home of the Texas Rangers), which offers checkout-free shopping in its apparel and merch shop.

Major retail and e-commerce players use AI to optimize worker tasks, inventory, and supply chain management. Walmart’s retail workers rely on an AI and augmented reality-powered application to determine what needs restocking, effectively place products on the shelves, and reduce trips to the backroom. The company also uses predictive analytics to determine which items will be in demand and when. This capability allows Walmart to optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and meet customer demand.
Likewise, the fashion retailer H&M uses AI to analyze store returns, receipts, and loyalty card data to better allocate inventory and predict what items will sell well in different stores. Through a detailed analysis of purchases and returns, H&M identified that its main clientele consisted of women. Surprisingly, items such as pastel-colored floral skirts and higher-priced products were selling better than anticipated. Consequently, the store has seen a notable improvement in sales, according to the Journal.
AI is also used for customer relationship management (CRM) and personalization. Leading beauty retailer Sephora leverages AI in its virtual artist app. The app personalizes the shopping experience by allowing customers to try different makeup products through smartphone cameras virtually. Similarly, Stitch Fix uses AI to tailor clothing selections to individual customer preferences. These selections improve as customers give feedback, creating a highly personalized shopping experience for greater customer retention.
The Impact of AI on the Retail Workforce
As the retail industry continuously adapts to customer expectations, it’s increasingly relying on AI to drive productivity and efficiency. While there are many concerns that AI will replace workers, one of its main benefits is to provide “an extra set of hands” as noted by Quartz. One such example of this increased productivity is Walmart’s use of a shelf-scanning robot. The robot takes on manual, repetitive tasks while associates assist customers. Likewise, luxury retailer Burberry uses AI chatbots to suggest similar products to shoppers for a more personalized buying experience.
Getting Started with AI: Take a Lifecycle Approach
Your organization has likely already uncovered multiple use cases for AI. With so many options, taking a deliberate approach to AI projects is essential to ensure that AI projects are done responsibly, resources are well-utilized, and projects deliver measurable, meaningful business benefits.
At Shibumi, we recommend taking the AI lifecycle approach to manage all AI projects through a consistent set of steps. This approach starts by identifying a few concrete business problems and generating AI solution ideas. Then, a small, qualified group will evaluate all proposed AI ideas and narrow the list down to just a few for prototyping. Prioritization decisions are based on the use cases’ value, feasibility, and risks.
This approach emphasizes the importance of developing prototype (or pilot) solutions first to validate the value hypotheses of AI use cases (“Will this AI solution increase this business KPI by Z percent?”) and using feedback from the pilot to decide the next steps (e.g., whether an AI solution is ready for wider implementation, needs refinement, or needs to be stopped altogether).
Once decision-makers decide that certain prototype solutions are worth implementing more widely, a small, interdisciplinary team identifies and addresses all potential implementation hurdles to maximize the solution’s chances of gaining traction. Finally, once a new AI solution is rolled out, a team monitors its usage and business benefits and makes adjustments to ensure it delivers the expected business value.
To effectively manage AI projects through their lifecycle, try Shibumi’s AI Value Accelerator. This software solution helps companies govern AI projects, manage them through their lifecycle, and drive measurable business value. The software helps you gather AI ideas from your workforce and manage them centrally, scoring and prioritizing ideas based on value, feasibility, and risk. It comes with out-of-the-box reports to help monitor benefits and ROI. Learn more about our AI Value Accelerator here.